SPLiT-seq combinatorial split-pool cellular decoding
This split-pool barcoding design enables many single-cell transcriptomes or epigenomes to be profiled together using combinatorial barcodes. The concept is essentially the same as the sciRNA-seq design, but the orientation of the cDNA and barcodes is inverted. The number of cells that can be profiled simultaneously scales exponentially with the number of rounds of barcoding. Barcode tags are appended sequentially in the initial RT step and in successive rounds of splitting and repooling of fixed cells. A UMI is included in the last round prior to cell lysis, and the last barcode is added during PCR amplification after cell lysis. Thus, cells are uniquely identified by their combination of cellular barcodes 1 to 4. The method is described in Single-cell profiling of the developing mouse brain and spinal cord with split-pool barcoding Rosenberg et al. Science 2018, 360:176-182 | DOI: 10.1126/science.aam8999 and Supplementary Materials
If the results are written to SAM, BAM or CRAM the raw uncorrected cellular barcode sequence is written to the CR auxiliary tag, the corresponding quality scores are written to the CY auxiliary tag, the corrected cellular barcode sequence is written to the CB auxiliary tag and the probability that the Cellular barcode decoding is incorrect is written to the XC auxiliary tag.
The uncorrected mollecular barcode (UMI) sequence is written to the RX auxiliary tag and the corresponding quality scores are written to the QX auxiliary tag.
Read Anatomy
The final PCR products submitted for sequencing are composed as follows:
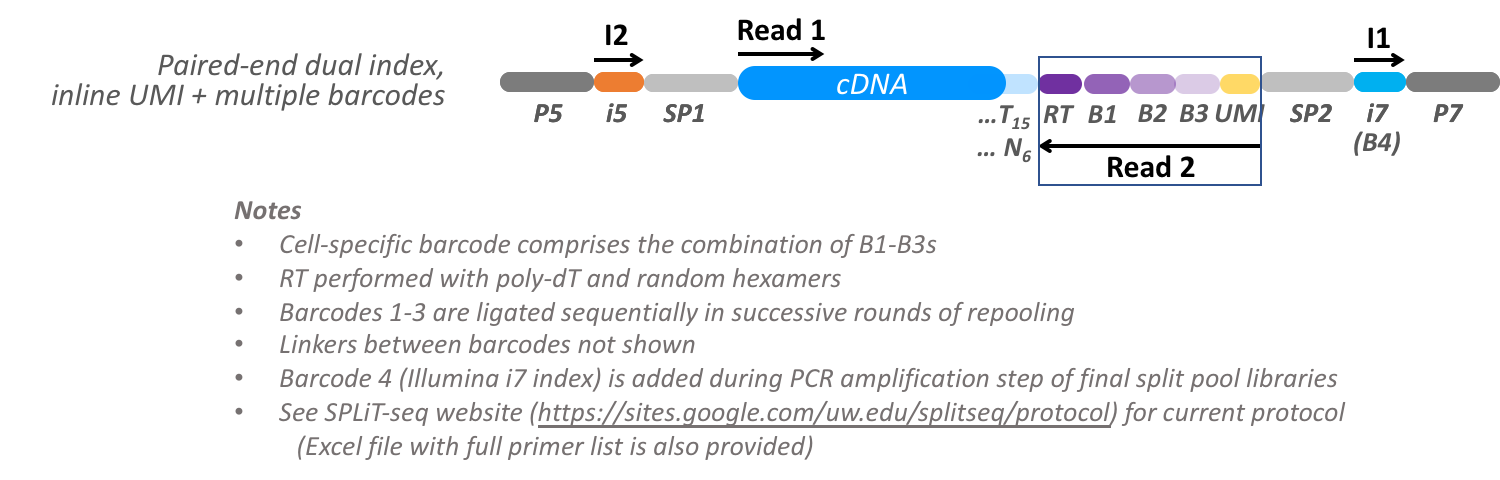
Input Read Layout
Base calling with bcl2fastq will produce 4 files per lane:
HGGKLBGX2_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz: Read 1, starting from the beginning of the insert fragment (“top” strand).HGGKLBGX2_L001_I1_001.fastq.gz: Index 1, the i7 index.HGGKLBGX2_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz: Read 2, starting from the other end of the insert fragment (“bottom” strand); note that this sequence is reverse complemented relative to the Read 1 sequence.
"input": [ "HGGKLBGX2_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz", "HGGKLBGX2_L001_I1_001.fastq.gz", "HGGKLBGX2_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz" ]declaring input read segments 2 biological and 2 technical sequences are often found in 4 FASTQ files produced by bcl2fastq base calling.
Read segments emerge from the sequencer in the same order as a simple dual-indexed run (R1, I1, I2, R2). We wish to extract the UMI (8bp) and RT barcode (10bp) from Read 1, the cDNA template sequence from Read 2 (50 bases), the i5 index (10bp) from the Index 2 read, and the i7 index (10bp) from the Index 1 read.
Token expression Segment index First Last Length Description 0::66006566template cDNA sequence on segment in R1 2::1020910UMI on segment in R2 2:86:94286938BC1: RT barcode on segment in R2 2:48:56248558BC2: ligated barcode on segment in R2 2:10:18210178BC3: ligated barcode on segment in R2 1::61056BC4: i7 sublibrary barcode on segment in I1 Tokenization patterns for decoding tha various artifacts of a SPLiT-seq protocol.
{ "cellular": [ { "algorithm": "pamld", "base": "rt_round_1", "comment": "BC1: First round cellular barcode", "confidence threshold": 0.99, "noise": 0.05, "transform": { "token": [ "2:86:94" ] } }, { "algorithm": "pamld", "base": "ligated_round_2", "comment": "BC2: Second round cellular barcode", "confidence threshold": 0.99, "noise": 0.05, "transform": { "token": [ "2:48:56" ] } }, { "algorithm": "pamld", "base": "ligated_round_3", "comment": "BC3: Third round cellular barcode", "confidence threshold": 0.99, "noise": 0.05, "transform": { "token": [ "2:10:18" ] } }, { "algorithm": "pamld", "base": "nextera_barcode", "comment": "BC4: Fourth round cellular barcode on the i7 index segment", "confidence threshold": 0.99, "noise": 0.05, "transform": { "knit": [ "~0" ], "token": [ "1:0:6" ] } } ], "import": [ "splitseq_core.json" ], "input": [ "HGGKLBGX2_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz", "HGGKLBGX2_L001_I1_001.fastq.gz", "HGGKLBGX2_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz" ], "molecular": [ { "comment": "The UMI is in the first 8 bases of Read 1", "transform": { "token": [ "2::10" ] } } ], "template": { "transform": { "token": [ "0::66" ] } } }decoding both combinatorial barcodes in one run splitseq_l01_cellular.json will decode both the RT and nextera barcodes in one run and populate the cellular and molecular SAM auxiliary tags. It will emit a single segment with the first 50 nucleotides on the fourth segment in R2. The list of possible values for the RT and nextera barcodes are defined in the imported splitseq_core.json configuration file and are used in splitseq_l01_cellular.json by inheritence using
"base": "rt_round_1","base": "ligated_round_2","base": "ligated_round_3"and"base": "nextera_barcode".